What Do It Mention When Baby Are in Anterior Position
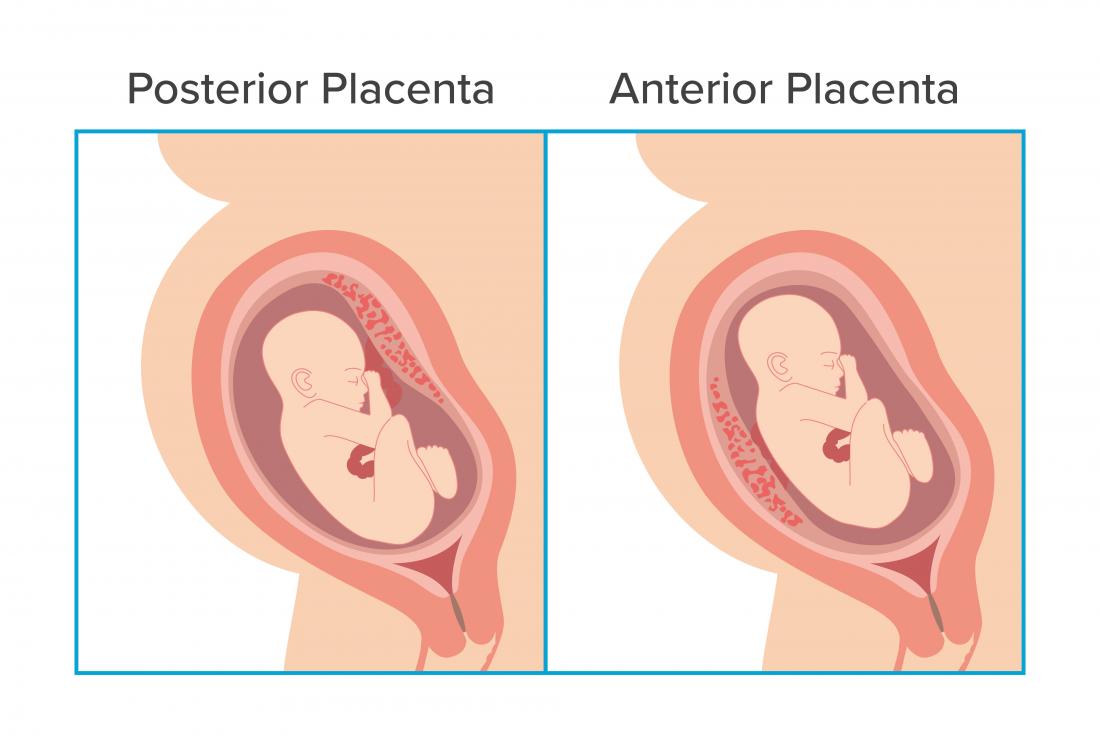
The placenta is an organ that grows in the uterus during pregnancy to supply the fetus with oxygen and nutrients. An inductive placenta is one that attaches to the front of the uterus.
The placenta may attach itself in any of the following positions:
- posterior (at the dorsum of the uterus)
- anterior (at the front of the uterus)
- on the side of the uterus
- fundal (at the top of the uterus)
- low-lying (at the bottom of the uterus and sometimes even over the cervix)
An anterior placenta by and large does not impact the pregnancy or health of the fetus. Still, information technology may change how a woman has medical checkups and sometimes increases certain risks. Learn more than in this article.
The placenta is an organ that grows in the uterus during pregnancy to nourish the baby with oxygen and nutrients via the umbilical string. The placenta attaches itself to the wall of the uterus. Anterior placenta is the medical term for a placenta that connects to the front of the uterus.
An anterior placenta volition sit down between the forepart of the tum and the fetus.
Most of the time, a fertilized egg volition implant on the back of the uterine wall. When this happens, the placenta generally forms along that wall also. Doctors refer to this as a posterior placenta.
Sometimes, having an anterior placenta may make it harder for a woman to feel fetal movements. In some cases, it tin can make it more than challenging for an obstetrician to detect a fetal heartbeat.
Generally, the positioning of the placenta does not affect the pregnancy or the fetus unless the placenta blocks the cervix, which is called placenta previa.
A woman with placenta previa may need to stay in the infirmary for monitoring, and she is likely to need to give birth via cesarean delivery.
All the same, an anterior placenta is non likely to bear upon the pregnancy or its management. The differences in a pregnancy with an inductive placenta are minor. Having an anterior placenta is quite common.
Due to the position of the placenta in front of the baby, a woman with an anterior placenta may not experience fetal move equally strongly as a woman with a posterior placenta, particularly earlier in pregnancy when the fetus is smaller.
In cases where a woman needs an amniocentesis, an inductive placenta may make it slightly more difficult for a doctor to comport out the test.
An amniocentesis is a process that takes a sample of the amniotic fluid surrounding the baby. A doc volition analyze the fluid for signs of any abnormalities.
They will perform this test by inserting a needle into the uterus via the woman's abdomen. The location of an inductive placenta at the forepart of the uterus may make this more challenging.
A doctor can determine the placement of the placenta using an ultrasound, which ordinarily occurs between 18 and twenty weeks of pregnancy.
During this ultrasound, a doctor volition examine the fetus and placenta for whatever abnormalities.
Sometimes, they may recommend additional ultrasounds closer to the delivery engagement to check the location of the placenta and ensure that it is not covering the cervix.
Although an anterior placenta is not usually a cause for concern, some studies have shown that the placement of a placenta could affect the outcome of the pregnancy.
Ane
- pregnancy-induced hypertension
- intrauterine growth restriction
- gestational diabetes
- placental abruption
- intrauterine fetal expiry
At that place is also some evidence to suggest that women with an inductive placenta take a college gamble of issues after the baby is born.
The placenta can also drift during pregnancy, pregnant that it starts growing in some other direction. An inductive placenta may migrate upward and adhere itself to the top of the uterus where many of the bigger claret vessels are present.
All pregnant women should see a md regularly throughout their pregnancy. While an anterior placenta will not usually crusade any issues, other symptoms tin signal a problem with the placenta.
A woman should call her doctor immediately if she notices any of the following symptoms:
- vaginal bleeding
- fast or constant contractions
- astringent back pain
- abdominal pain
- decreased fetal motility
- firmness in the uterus
The symptoms of a placental problem tend to begin suddenly, and they are oft severe.
An anterior placenta occurs when the placenta grows in the front end of the uterine wall. An inductive placenta is not typically a cause for concern. Most of the time, it does not touch on the outcome or direction of a pregnancy.
It may, nonetheless, go far more difficult for a adult female to feel fetal movements or for a doc to observe the fetus's heartbeat.
A woman should consult her doctor regarding any concerns about the pregnancy or signs of problems relating to the placenta. Regular prenatal care can help prevent or manage potential complications.
collinssuposincer.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/324554
0 Response to "What Do It Mention When Baby Are in Anterior Position"
Post a Comment